CEFIPRA 2023
Data reduction and surrogate modelling of transition to turbulence of Rayleigh-Taylor instability data obtained by DNS
Project identity
This is CEFIPRA funded project working with Prof Aditi Sengupta and Tapan Sengupta from IIT(ISM) Dhanbad, India
- Dates: 2023-2026
- Keywords: RTI, extreme scale computing, data reduction
- Goals:
- Advance computing of FOM
- Enhance physics understanding
- Enable data reduction for very lage datasets
- Develop surrogate models of RTI instability
- Key outcomes
- 2 Oral communications: DTE-AICOMAS 2025 and SIAM PP26
- 3 physical meetings
- 1 published paper Joshi et al. PDF
- 1 paper submitted to Computational Physics Communication : Ajanif et al
Abstract
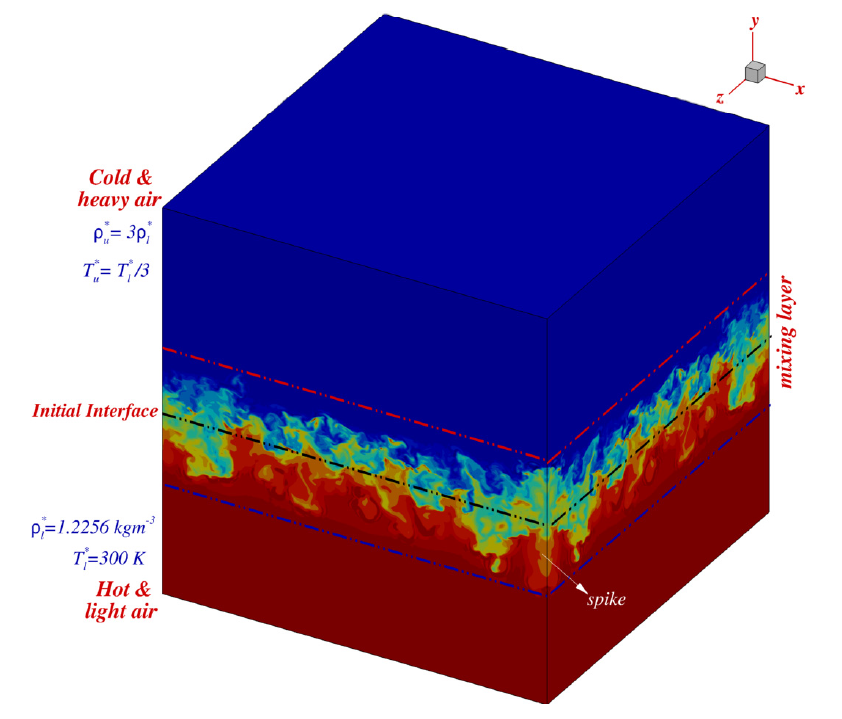
It is now understood that many problems of fluid mechanics have been solved satisfactorily, except the problem of turbulence. In recent days, even this problem is understood for wall-bounded flows and some other periodic problems. Understanding the physics and the route of transition to turbulence is not well understood from flow control perspective for free shear layers, as in the case of Rayleigh-Taylor instability (RTI). Thus, solving the problem of Rayleigh-Taylor instability by direct numerical simulation (DNS) has been taken up. This is being pursued by solving compressible three-dimensional Navier-Stokes equations employing high accuracy DNS methodologies (using in-house developed code) of HPC that use 4.19 billion points with commensurate small time steps. However, the DNS data is of size 160GB at each instant of time. Rendering such data is a huge challenge, not only for visualization itself, but also post-processing such data sets using techniques to characterize the nonlinear instability of the transition to turbulence. In this process, reduced data and surrogate models developed by the French side would be of tremendous value. Thus, in this proposal, generating the data by DNS (first step that has been already started) is as important as the concurrent development of the surrogate model and its subsequent use in unravelling the transition to turbulence of the RTI.
Physical meetings
